Mastectomy
Mastectomy is the complete removal of the entire breast tissue including the nipple areolar complex. (NAC)
It is a surgical option offered to patient diagnosed with breast cancer or as a prophylaxis to reduce risk of breast cancer in high-risk women.
Breast Anatomy
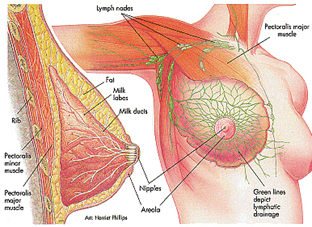
Breast tissue extends from the 2nd rib below the collar bone till the level of the 6th rib and from the outer edge of sternum and laterally till edge of the lattisimus dorsi muscle
Criteria for Mastectomy
- Patients who are contra-indicated for breast conserving surgery *
- Patients who prefer/advised for mastectomy
- Prophylaxis breast cancer surgery for patients with BRCA Gene positive
Contraindications for BCS
- Multicentric breast cancer with more that 2 breast cancer lesions in more than 1 breast quadrant
- Large tumour size in relation to breast size
- Diffuse extensive malignant microcalcifications on MMG
- History of previous breast radiation therapy
Types of Mastectomy
- Radical Mastectomy: Extensive surgery with removal of breast tissue, chest wall muscle pectoralis major and minor muscle and Level 1-3 axillary dissection (rarely practiced these days)
- Modified Radical Mastectomy: Removal of the breast tissue, fascia of the chest wall muscle, Level 1-2 axillary dissection
- Simple/Total Mastectomy: Removal of the entire breast tissue only without axillary dissection
- Skin–sparing Mastectomy (SSM): Removal of the entire breast tissue including the Nipple areolar complex preserving most of the natural breast skin envelope to allow for reconstruction
- Nipple-sparing Mastectomy (NSM): Removal of the entire breast tissue preserving the nipple areola complex and the entire natural breast skin envelope to allow for breast reconstruction. Cancer should not be less than 2cm near to the nipple for nipple preservation
- Areolar-sparing Mastectomy (ASM): Removal of the nipple and sparing the pigmented areolar to give a more appealing visual appearance of the breast. Nipple has to be removed in these cases as the tumor with within 2cm to the nipple areolar complex.
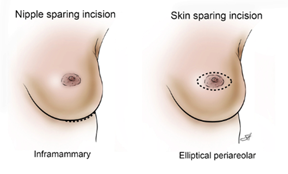
Credit Source : Baylor college of medicine
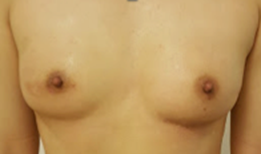
Nipple Sparing Mastectomy with tissue flap reconstruction
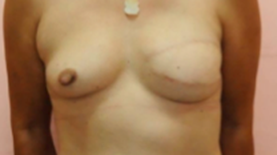
Skin Sparing Mastectomy with TRAM flap reconstruction
Choice of Mastectomy
- No immediate reconstruction – Total mastectomy or Modified radical mastectomy
- Immediate reconstruction – Nipple sparing mastectomy , skin-sparing mastectomy or areolar sparing mastectomy with Autologous tissue flap reconstruction
Total Mastectomy – The Procedure
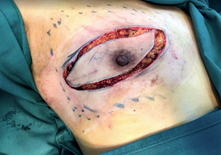
Transverse / oblique elliptical incision is made to include the tumor mass and the nipple areola complex
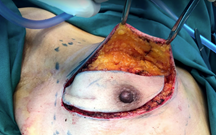
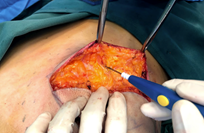
Upper and lower skin flaps are raised
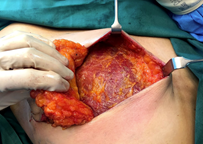
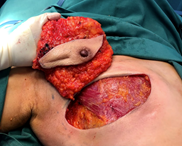
The breast tissue is dissected from the chest wall
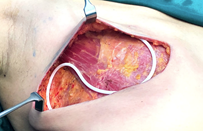
Closed suction drain is placed within the cavity for drainage of the serous fluid.
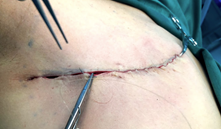
The upper and lower skin flaps are approximated and sutured with absorbable stitches not seen externally and need not be removed
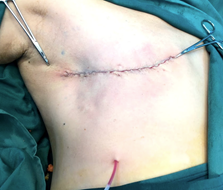
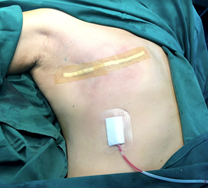
The wound is covered with an adhesive dressing.
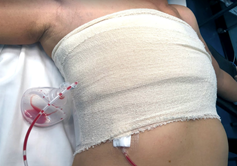
Compression dressing is applied with crepe bandage to reduce hemoserous collection.
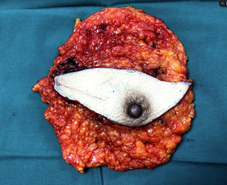
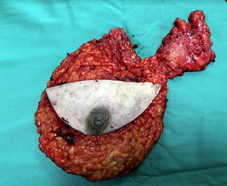
Breast tissue removed Breast and Axillary tissue removed
Complications after mastectomy (Breast cancer surgery complications)
- Seroma formation – the drainage tube is left in place until the drainage of serous fluid has reduced to less than 30mls over 24hour period
- Wound Infection – increased risk in those who smoke, who are immunocompromised and uncontrolled diabetes
- Hematoma / Blood clot – increased risk in those taking anticoagulant. If the hematoma is expanding, then sometimes it is necessary to take back to surgery to remove the blood clot and stop the bleeding in theatre
- Skin Flap Necrosis – if the skin flaps are dissected to thin and devoid of blood supply
- Breast Pain
- Arm Morbidity
